|
|
|
|
A move to test our ability and our will to resist. President Truman, speaking in 1949
The climax of the struggle for power over Germany and Europe. Avi Shlaim, Britain, the Berlin Blockade and the Cold War (1983)
The first major crisis of the Cold War, setting up the stage for the decades of tension that were to follow. Rebecca Byrnes (an Australian student) on Suite 101.com
The first point where war between the two superpowers was possible. ‘Booji’, a contributor to www.debatewise.com
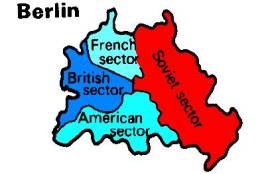
The USSR had already disagreed with Britain and the USA at Potsdam (July 1945) about what should be done with Germany. Germany had been split into four zones. There had been particular disagreement about reparations: Britain and America had wanted Germany to recover economically, but the Russians had gained the right to take 10% of the industrial equipment of western Germany, and as whatever they wanted from their own zone in eastern Germany:
Berlin was also split into 4 zones. But Berlin was entirely within - and surrounded by - the Russian zone.
Consider:1. Think of as many reasons as you can why, in the period 1945-49, Germany was often at the centre of the Cold War. 2. Discuss all the reasons you can think of why Stalin blockaded Berlin. Rank them in order. Compare your list to the explanations offered by the Soviets.
|
Going DeeperThe following links will help you widen your knowledge: Berlin Blockade web sites: Germany in the Cold War - basic overview
US State Department memo (pdf) setting out the US position Telegram (pdf) from A Paniushkin, Soviet ambassador to the US, setting out the Soviet position After Victory - an interview with Stalin in the Russian newspaper Pravda, October 1948.
NATO - essential reading
Flim clips and YouTube: Berlin Airlift - BBC 20thC History (first 10 mins)
|
What caused it? [CABAN]
Source B[The Americans had introduced a new currency into Berlin.] Old money flooded into the Soviet Zone. Some restrictions were placed on links between Berlin and western zones, but the Soviet side was ready to supply food to all Berlin. Yet every day 380 American planes flew into Berlin. It was simply a propaganda move intended to make the cold war worse. From a Russian history book.
|
Source ABritain and America tried to restore German prosperity in their sectors, but the Russians systematically looted their zone. This Low cartoon of October 1946 shows Bevin (British foreign minister) and Byrnes (America) trying to get the lorry of a 'united Germany' going, while the Russian foreign minister Molotov sits smugly on his motorbike, having stolen the wheels - 'Pity you fellows can't get your part going. I fixed mine OK', he is saying. Click here for the interpretation
Source CThis cartoon by the British cartoonist Illingworth appeared in the Daily Mail on 9 September 1948. Stalin has blocked the mousehole, and toys with a mouse labelled 'Berliners', whilst the other 'western powers' scuttle around in alarm. Click here for the interpretation
|
What happened?The American Army wanted to fight its way into Berlin – that would have caused a war. Instead, Truman decided to supply Berlin by air. The situation was bad at first, but things got better (pdf) as the blockade went on. On 12 May 1949, Stalin re-opened the borders.
Airlift Facts
Consider:3. Working as a whole class, draw a spidergram to show all the reasons why the Berlin blockade failed. 4 What were the results of the Berlin Blockade? 5. How close, do you reckon, did the Berlin Blockade come to a third world war?
|
Source DThis cartoon of 14 July 1948 by EH Shepard for the British magazine Punch shows Stalin watching as storks fly coal and food into Berlin. Click here for the interpretation
|
What were the Results? [CENA]
|
Source EThe crisis was planned in Washington behind a smokescreen of anti-Soviet propaganda... The self-blockade of the Western powers hit the West Berlin population with harshness. The people were freezing and starving. In the Spring of 1949 the USA was forced to yield. From a Russian history book.
Source FWe demonstrated to the people of Europe that we would act resolutely, when their freedom was threatened. Politically it brought the people of Western Europe closer to us. President Truman, speaking in 1949.
Source GNeither side gained anything. The USSR had not gained control of Berlin. The West had no guarantees that land communications would not be cut again. Above all confrontation made both sides even more stubborn. Historian Jack Watson writing in 1984.
|
NATO AND THE ESCALATION OF TENSION [CRIMES]The creation of NATO significantly increased international tension between East and West in the 1950s: 1. Containment• NATO's network of allies with a mutual agreement to go to war if any one of them were attacked reinforced Soviet fears of Western encirclement. • Working with NATO was a key part of President Eisenhower’s ‘New Look’ US foreign policy (1953), which sought to replace confrontation with espionage and deterrence; this further heightened tensions. 2. Rearmament and Arms Race• West Germany's NATO membership (1955) alarmed the USSR, leading to increased Soviet military buildup in Eastern Europe. • NATO’s decision to rearm and include nuclear weapons in its strategy (1954) escalated the arms race, with the USSR responding by developing its own hydrogen bomb (1955). 3. Intervention in Conflicts• During the Korean War (1950–1953) the US massively increased its military assistance to NATO, restructuring its organization, and expanding its membership to include Greece, Turkey, and West Germany. This led the USSR to support North Korea and China, intensifying East-West confrontation. 4. Military Blocs• NATO's creation prompted the USSR to form the Warsaw Pact in 1955, thus solidifying the division of Europe into two opposing military blocs. 5. Emboldened the US• NATO emboldened the US to oppose Soviet demands on Berlin, leading to the Berlin Crisis of 1958-61. 6. Strategic Bases• The establishment of NATO bases in Turkey and Greece (both joined in 1952) positioned Western forces closer to Soviet borders, increasing Soviet fears and rearmament. • US nuclear-capable bombers were stationed in Europe under NATO coordination, making Soviet cities potential immediate targets.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Spotted an error on this page? Broken link? Anything missing? Let me know. |
|